By using radio waves to automatically transmit data to a tag reader, Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) tracking ensures automatic identification of products, cartons, cases, and physical assets. An effective RFID tracking system can help provide visibility throughout its entire lifecycle. This additional layer of data can prove valuable for various industry-specific situations, including: foodservice operators gathering fresh ingredients for a menu; hospitals tracking surgical tools to aid in sterilization methods; and apparel brands ensuring complete and accurate orders are received by retailers.
Tracking Your Assets Using RFID
More About RFID
What Are the Benefits of Using RFID to Track Your Products?
Barcode Tracking vs. RFID Tracking
While some may think they have to choose one over the other, barcodes and RFID can complement each other. The same data encoded in case/carton barcodes can be made available wirelessly and captured automatically through RFID. This can be a key building block in creating interoperable solutions that serve multiple business processes across multiple supply chain trade partners, automating the capture of key data elements across the supply chain.
When considering an RFID tracking system, it is important to consider your use cases and the return on investment. Also, your trading partners’ capabilities, both upstream and downstream, should be considered before any final decisions are made.
One of the main benefits of using RFID to track your products is that it doesn’t require a line of sight. A reader can either be handheld or “fixed.” Fixed readers are designed to read RFID tags on items as they pass by or are placed within the read range. This allows for the reader to continuously scan for tagged items without needing a person to manually do the scanning.
How Does RFID Asset Tracking Work?
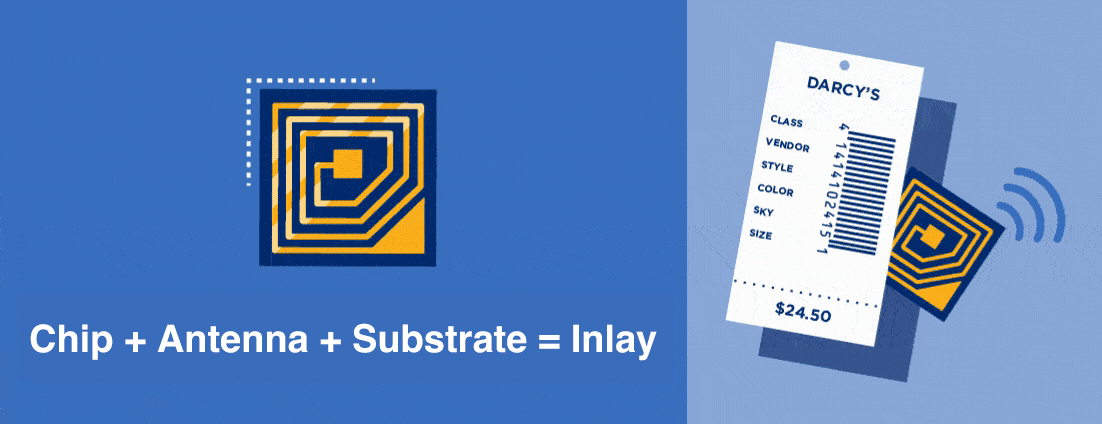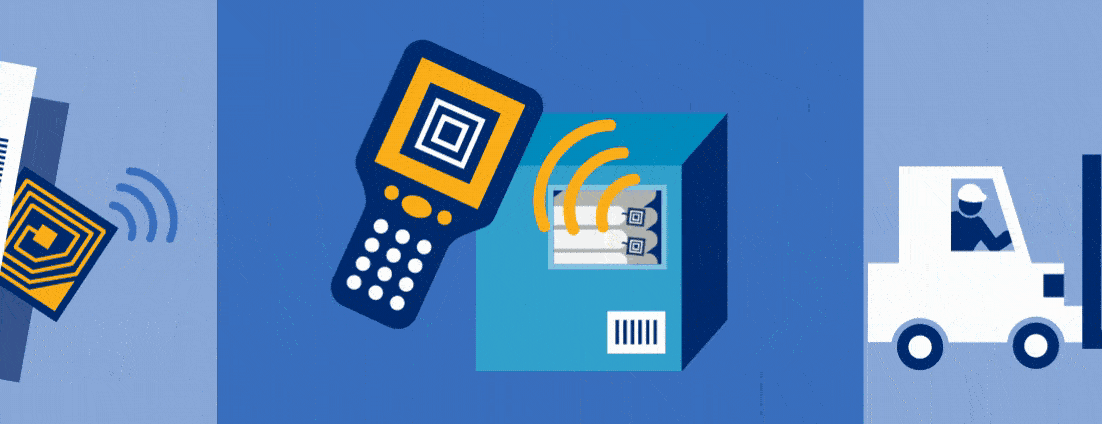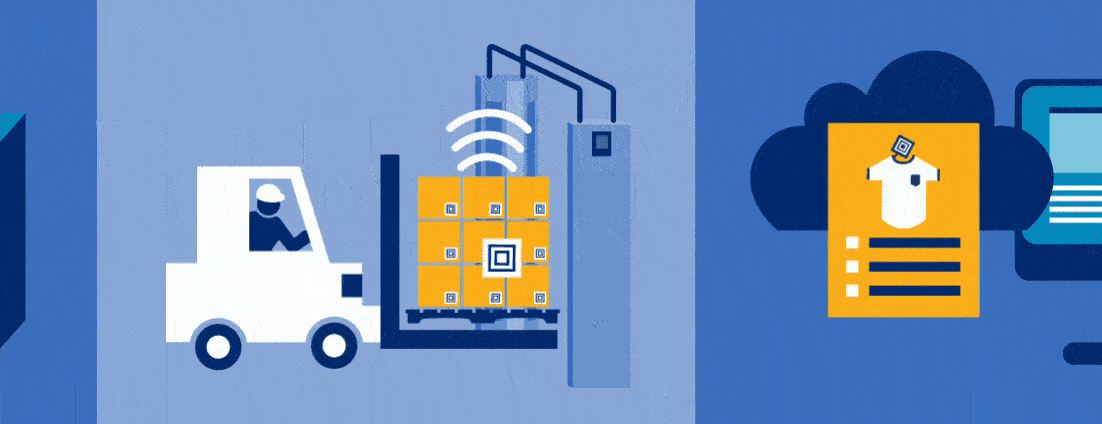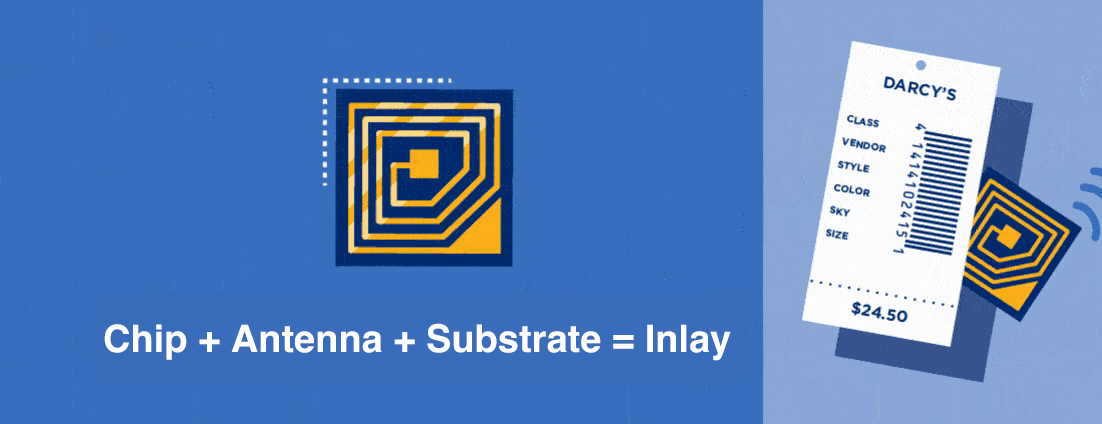
One example of an RFID tracking system at work can be seen in warehouses. When a warehouse facility or retailer back end is set up with a read point at its loading dock, cartons and cases that are RFID-tagged can be automatically captured as they are unloaded from the delivery truck.
Active RFID Tags
An active tag has an internal power source. The power source and tag are self-contained as a single unit, enabling it to continuously communicate with a reader.
Passive RFID Tags
In contrast to an active tag, a passive tag doesn’t have its own power source. Instead, it is powered by being in proximity to a reader. The electromagnetic field provides energy that powers up the passive tag. When the passive tag activates, it can transmit, or backscatter, data to the reader.


